Backing up corporate data is an essential practice for ensuring business continuity, protecting sensitive information and minimizing the risk of data loss. Over time, backup methods have undergone significant evolution, aided by technological advances, enabling companies to better manage their data efficiently, securely and cost-effectively.
History and importance of backup
The history of corporate data backup goes back to the first backup methods based on the use of magnetic tapes. These tapes were commonly used to store data and perform regular backups. However, with the advent of hard disks, companies quickly migrated to this technology for faster, more reliable backups.
The years 1990-2000 saw the emergence of optical media such as CDs and DVDs, offering greater storage capacities than floppy disks. In the late 1990s, network-attached storage (NAS) systems made it possible to centralize backups on a shared device, simplifying data management. Later, in the 2000s, automated tape libraries emerged, facilitating efficient backups and the management of large quantities of data.
The adoption of the Cloud in the 2010s transformed the way companies store their data, offering a secure remote backup solution. Advanced backup methods, such as incremental and differential backups, have reduced the amount of data backed up in each cycle, improving efficiency. Real-time backup systems have eliminated the need for scheduled backups, enabling companies to protect their data continuously.
In addition, technologies such as snapshotting have emerged, enabling data snapshots to be created for rapid recovery in the event of a problem. Today, artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analysis are being integrated to anticipate backup needs, optimize resources and improve data protection.
The importance of backing up your data
Data backup is crucial for a number of reasons:
- Keeping control of your data: By making regular backups, you reduce the risk of accidental or malicious data loss, enabling you to maintain the integrity of your information.
- Ensure rapid business recovery: In the event of computer system downtime due to hardware error or attack, a well-planned backup enables rapid recovery, minimizing downtime.
- Last line of defense against attacks: Backups often serve as a last line of defense against cyberattacks such as ransomware, enabling data to be restored without paying a ransom.
There are different types of data backup
Full backup, Incremental backup, differential backup
- Full backup
This method involves copying all the files and folders on a system with each backup. Each backup stores the data source in its entirety, guaranteeing rapid restoration should the need arise. However, this method requires more time and storage space. - Incremental backup
An incremental backup only records changes made since the last full backup. It is faster to perform, but restoration may be slower. - Differential backup
Differential backup stores changes relative to the last full backup, offering a balance between backup speed and restoration.
File backup vs. image backup
File backup protects critical data from accidental deletion, corruption or loss. It is ideal for user-generated files, and enables faster recovery with less storage space.
Image backups, on the other hand, capture the complete state of a system at a given point in time, enabling full restoration when needed, eliminating the need to determine which files need to be backed up/restored.
Storage locations
The 3-2-1 rule, the standard for data protection and disaster recovery since 2005, recommends having three copies of your data, two different types of media for backups and at least one off-site backup file. This approach strengthens data resilience in the event of a disaster.
However, in the face of modern challenges, a 3-2-2 strategy is recommended, adding a second storage location in the cloud for added protection against ransomware and other threats.
Storage frequency
The “Grandfather-Father-Son Backup” method, based on data backup rotation, offers a hierarchical solution for data backup, ranging from annual to daily backups. This approach makes it easier to manage data retention requirements and contingency plans.
Mistakes and best practices
Common mistakes to avoid with backups include synchronization within the same network, reliance on a single local copy, use of physical media without redundancy, lack of recovery testing and failure to check the “health” of backup copies.
Best practices in cybersecurity and backup include the use of data encryption, immutable and isolated backups, an adequate number of backup copies and the choice of a secure location, such as a certified data center.
Our backup solution
We’ve been working with Veeam, a leader in backup solutions, for seven years running. According to IDC data, Veeam backup solutions are distinguished by their efficiency. They restore SaaS applications ten times faster, restore business five times faster, and generate average annual savings of $1.1 million.
Veeam also offers MScloud Secure, a backup solution that makes it easy to manage your environment while guaranteeing the protection of your corporate data. This solution offers a transparent and flexible implementation in the cloud, adapted to the hybrid work context. What’s more, it stands out as a Quebec-based solution, with the distinctive feature of storing your data in duplicate in two Tier III data centers located in the Quebec City region. This secure approach ensures compliance with local standards and regulations.
Data security is a priority, and our secure cloud solution features end-to-end encryption to ensure absolute data protection, whether at source, during transfer or in the cloud backup space. Your backed-up data is thus protected against malicious attacks by cybercriminals and accidental deletion, guaranteeing the longevity of your crucial information.
Backup for M365
Microsoft 365 users should be aware that Microsoft does not back up their data, exposing businesses to the risk of data loss. You can find out more about data backup in Microsoft 365 in our dedicated article.
Backup solutions tailored to Microsoft 365, such as those offered by Veeam, ensure data security and recovery, particularly for Teams and SharePoint.
How to choose the right backup solution?
The choice of a backup solution depends on your organization’s tolerance to outages and data loss. You need to determine how long your organization can afford to be down in the event of data loss.
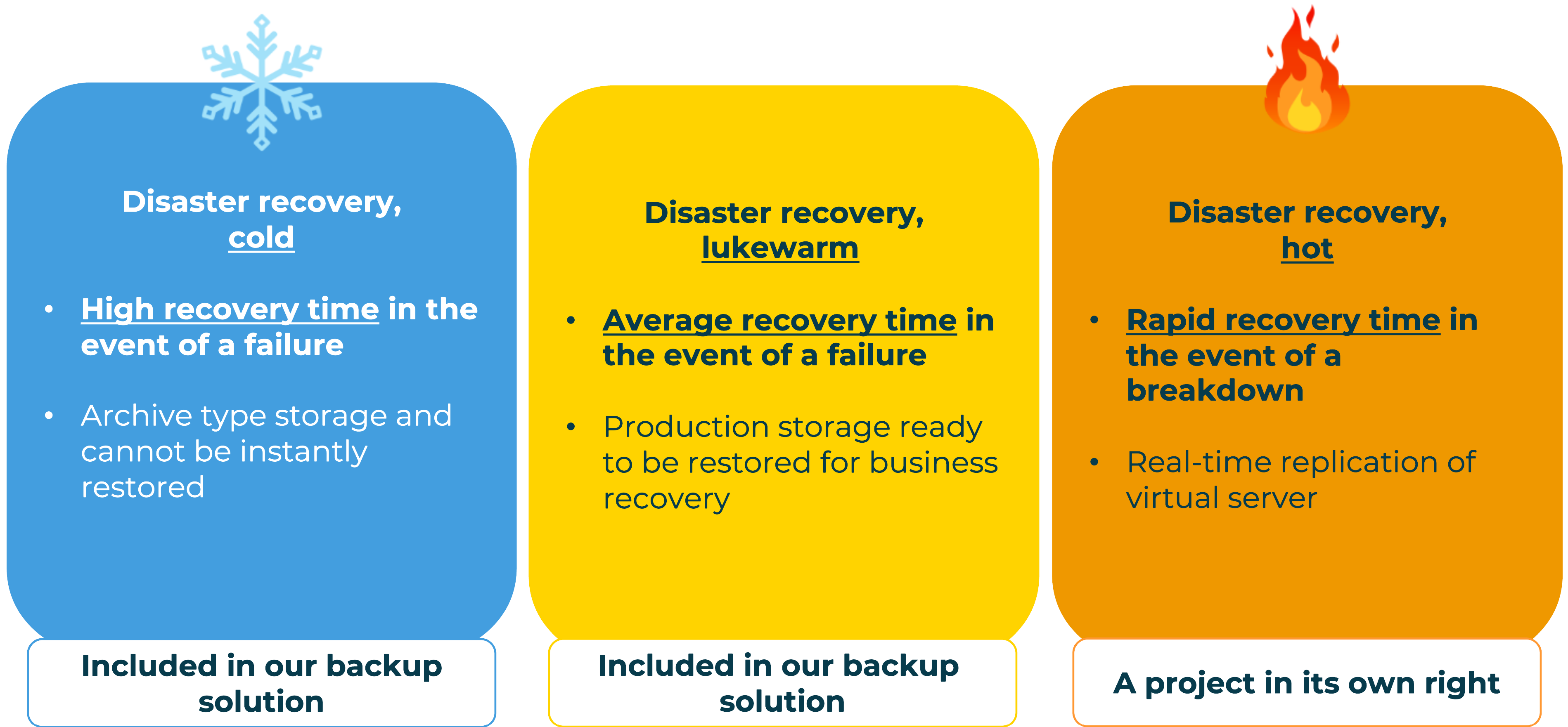
Disaster recovery
IT disaster recovery aims to quickly restart operations. Different types of disaster recovery, from “cold” to “hot”, offer different recovery times, depending on business needs.
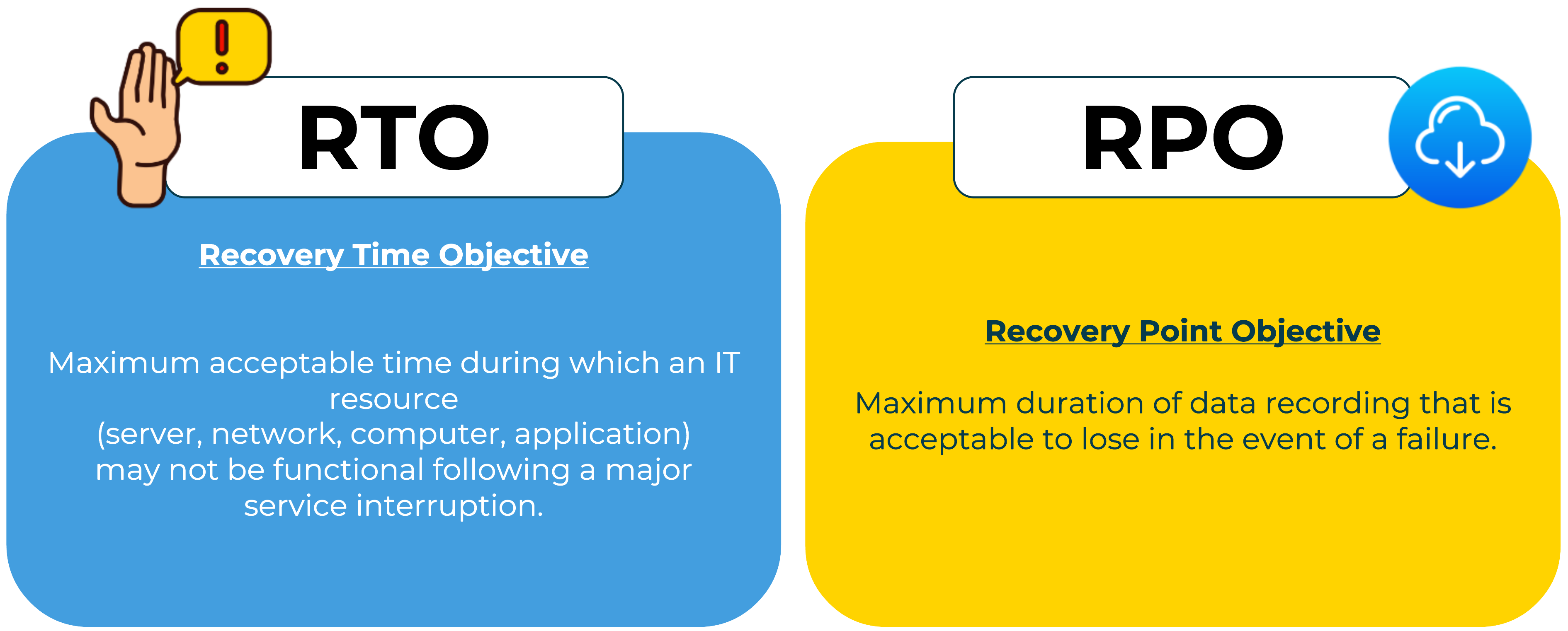
Key disaster indicators
Key indicators in the event of a disaster include the Recovery Time Objective (RTO), which represents the maximum acceptable downtime, and the Recovery Point Objective (RPO), which represents the maximum acceptable data save time.
Why choose MS Solutions for your business recovery?
MS Solutions offers a complete solution for IT backup and disaster recovery. All workloads, from VMware to Microsoft Azure, can be accommodated, guaranteeing data security and rapid recovery. The cost depends on the number of servers, workstations, M365 users and the amount of storage required to meet retention needs.
In brief
Backup and disaster recovery are crucial to any business. Evolving backup methods, combined with good cybersecurity practices, ensure data protection and business continuity, even in the face of modern challenges.
This article features content discussed in a previous webinar. To watch a replay of that webinar, click here. Subscribe to our newsletter to receive invitations to future webinars.